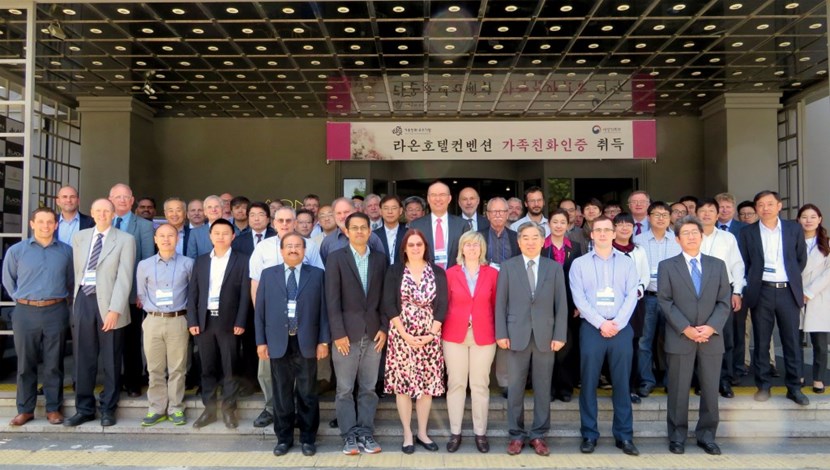
The fifth IAEA DEMO Programme Workshop (DPW-5) was hosted by the Republic of Korea through the National Fusion Research Institute. Previous workshops in the series were held in Los Angeles (2012), Vienna (2013), Hefei (2015) and Karlsruhe (2016).
More than 60 top fusion scientists and engineers from around the world gathered at the
5th IAEA DEMO Programme Workshop in Daejeon, South Korea, from 7 to 10 May, to discuss critical issues and next steps on the road to the realization of fusion energy.
While science and technology issues for fusion power are broadly agreed upon, upscaling the technology to commercial electricity generation is still decades away. This workshop aimed to help experts define the facilities and activities that can lead to the resolution of some of the key scientific and technological challenges to developing a demonstration fusion power plant (DEMO).
DEMO would show that controlled nuclear fusion can generate net electrical power and mark the final step before the construction of a commercial fusion power plant. DEMO is the machine that would explore continuous or near-continuous (steady-state) operation, tritium fuel self-sufficiency, and the large-scale production of energy and its conversion to electricity.
The ITER Members are exploring different routes:
China has made significant progress in planning for a device called China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (
CFETR) that would bridge the gaps between ITER and DEMO. Construction of the CFETR could start at around 2020 and be followed by construction of a DEMO in the 2030s.
The
European Union and
Japan are jointly building a powerful tokamak called JT-60SA in Naka, Japan, as a complement to ITER on a privileged partnership called the
Broader Approach. In addition to constructing the JT-60SA, the joint program consists of two other projects, the Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activities for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility (
IFMIF/EVEDA), and the International Fusion Energy Research Centre (
IFERC). This partnership represents a well-integrated approach to support ITER and to prepare to undertake the engineering design and construction of a subsequent DEMO. (More information on the European roadmap to fusion electricity, including the Broader Approach, can be found
here.)
India has announced plans to begin building a device called
SST-2 to develop components for a DEMO around 2027, and then start construction of a DEMO in 2037.
South Korea initiated a conceptual design study for a
K-DEMO in 2012 targeting the construction by 2037 with potential for electricity generation starting in 2050. In its first phase (2037-2050), K-DEMO will develop and test components and then utilize these components in the second phase after 2050 to demonstrate net electricity generation.
Russia plans the development of a fusion-fission hybrid facility called DEMO fusion neutron source (
FNS), a reactor that would harvest the fusion-produced neutrons to turn uranium into nuclear fuel and destroy radioactive waste. The DEMO-FNS is planned to be built by 2023, and is part of Russia's fast-track strategy to a fusion power plant by 2050.
The United States of America is considering an intermediate step called Fusion Nuclear Science Facility (FNSF) to be used for the development and testing of fusion materials and components for a DEMO-type reactor. Plans call for operation to start after 2030, and construction of a DEMO after 2050.
The IAEA is providing a platform for information sharing and exchange in order to facilitate nuclear fusion research and the development of technology. This is a role the IAEA has continuously played over the years—acting as a central hub for collaboration among countries working first on the
INTOR project, then ITER, and now DEMO.
Main findings and discussions from the IAEA DEMO Programme Workshop series can be found here.
Follow this link to the original article, which was published on the IAEA website on 11 May.