Cryopumps: fewer, cheaper and no less efficient
20 Jul 2012
-
Robert Arnoux
In the pre-2001 design, when ITER was to be nearly the size of Saint-Peter's Basilica in Rome, 16 cryopumps were to be accommodated at the divertor level of the vacuum vessel.
Cryopumps have the essential function of removing impurities and helium ash from the plasma, enabling the plasma to continue to burn and produce fusion power.
The requirements for vacuum pumping are linked to the plasma fuelling rates—even in the "smaller" ITER these had to be maintained. Design developments in cryo-pumping allowed the machine to be optimized with ten cryopumps in 2001 and eight in 2003.
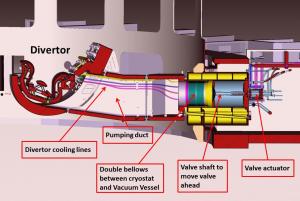
Eight cryopumps has been the Baseline design figure until recently, when the ITER Director-General proposed to simplify the divertor ports of the machine and remove all "T-shaped" branch ducts. This left only five or six positions where cryopumps could be placed.
This bold proposal was quite a challenge for the ITER vacuum team. "Let's say our creativity was strongly stimulated..." recounts ITER Vacuum Section Head, Robert Pearce. "A five-pump solution was proposed, but this was considered rather risky for the goal of achieving ITER's fusion power mission."
Following discussions at the Science and Technology Advisory Committee (STAC) in November 2011 and at the Ninth ITER Council later that month, a much improved solution was found: there would be six divertor cryopumps in ITER doing the job that was originally assigned to sixteen.
"Basically, improvements in the cryopumping system design over many years have allowed the cryopumps to sit in bigger housings, enabling them to pump longer and store more gas and impurities," says Robert. The new housings are "simpler" and have a volume of greater than 14 m³, as compared to 8 m³ in 2003. As the pumping configuration at the bottom of the machine (divertor level) was changed, it became possible to make improvements that resulted in the easier integration of other systems.
"We think that the overall six-pump solution is better in the end: we now have six identical systems. Operations are made simpler and the performance of the system is not affected," conclude Robert and his vacuum team.
Considering that each branch duct and cryopump is a multimillion-euro component, the savings for the ITER Project are considerable.