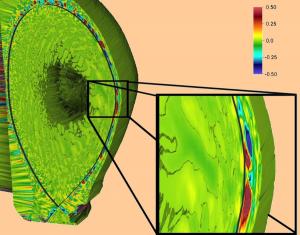
The bleeding "edge" of fusion research
25 Mar 2014
-
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Few problems have vexed physicists like fusion, the process by which stars fuel themselves and by which researchers on Earth hope to create the energy source of the future.
By heating the hydrogen isotopes tritium and deuterium to more than five times the temperature of the Sun's core, scientists create a reaction that could eventually produce electricity. Turns out, however, that confining the engine of a star to a manmade vessel and using it to produce energy is tricky business.
Big problems, such as this one, require big solutions. Luckily, few solutions are bigger than Titan, the Department of Energy's flagship Cray XK7 supercomputer managed by the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility.
Titan allows advanced scientific applications to reach unprecedented speeds, enabling scientific breakthroughs faster than ever with only a marginal increase in power consumption. This unique marriage of number-crunching hardware enables Titan, located at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), to reach a peak performance of 27 petaflops to claim the title of the world's fastest computer dedicated solely to scientific research.
See the original article and the computer visualization on the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility website.