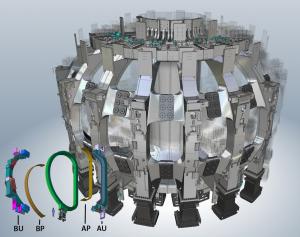
The most critical technical issue during manufacturing is the tightness of tolerances—just a few millimetres for components that, once assembled, measure 16 metres in height and 9 metres in width. Specialized welding techniques have been optimized to control distortion during the welding of steel plates that range from 6 to 40 cm in thickness.
The closure welding process—which will intervene after the winding packs have been inserted—is in the planning stages, with a mockup test and computer simulation underway to estimate and correct welding deformation. Tolerances of a few millimetres are required on the coil cases for proper assembly in the tokamak.
At Mitsubishi Heavy Industries in Kobe, coil case segments are now produced in series and the first inboard (AU) sub-assemblies have been assembled and welded.
Manufacturing is on schedule for the shipment in 2017 of the first completed case to Europe, where contractors will carry out the insertion of the first European winding pack and closure welding. Of 19 coil cases produced by Japanese contractors in the coming years, 10 will be shipped to Europe (the nine others will accommodate toroidal field winding packs produced in Japan).
The first completed toroidal field coil will reach the ITER site in 2018, shipped by the Japanese Domestic Agency.