Japan qualifies second outer vertical target
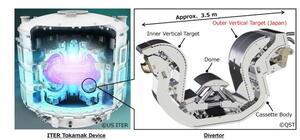
After working with a domestic manufacturer to qualify a first outer vertical target for the ITER divertor in 2024, Japan's National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST) successfully worked with a second manufacturer, Hitachi Ltd., to develop and qualify a second full-scale mockup of this critical plasma-facing component. The divertor targets—the dome (produced by Russia), the inner vertical target (produced by Europe) and the outer vertical target produced in Japan—face the highest head loads of the ITER machine.
The divertor is one of the most important components in a tokamak, as it plays a role in maintaining the stability of the nuclear fusion reaction by exhausting impurities such as fuel residue and helium. The divertor must be designed to withstand direct heat and particle load from the plasma. The armour material, tungsten, has been chosen for its high melting point, but the shape of the plasma-facing surfaces is also important. High precision machining and assembly technologies are required to achieve the correct overall shape, inclination, steps and gaps within tolerances of 0.5 mm or less.
The heat load on divertor targets can reach 20 MW per square metre—equivalent to the surface heat load that an asteroid probe is exposed to when re-entering the atmosphere and much higher than the surface heat load sustained by the Space Shuttle.
Beginning in 2022, Hitachi and QST began developing a second full-scale outer vertical target markup. Hitachi called upon its experience in the nuclear field, employing the high-quality welding technology for special materials and non-destructive inspection technology developed for restricted and complex shapes to achieve the high-precision machining and assembly required by ITER. The prototype was completed in March 2025 and in July, a high-heat-load sample of an outer vertical target passed the rigorous certification test demanded by the ITER Organization.
In total, QST is responsible for delivering 58 outer vertical targets to the ITER Organization.
Read the QST press release dated July 2025 in Japanese or English.