Image of the week
Bullseye
9 Jul 2018
Two perfectly circular structures, looking a lot like archery targets, have been installed on the west-facing wall of the Tokamak Complex.
Two large circular openings (not yet visible) will allow power to reach ITER's two heating neutral beam injectors. Today, we can see the opening reserved for a third provisional heating injector (at right) and a smaller "penetration" at left for the diagnostics neutral beam injector.
They are not for shooting, however. The target-like structures mark what will be openings in the concrete for high voltage transmission lines to feed power to the neutral beam injectors.
Injecting high-energy neutral particles into the plasma is the most powerful way to heat it. ITER will be equipped with two heating neutral beam injectors (with a provision for a third) and a neutral beam line for diagnostic purposes.
Neutral beam injectors are massive devices, as large as a school bus, that require considerable electrical power to operate. The transmission lines that will go through the circular opening (one for each injector) will carry extremely high voltage (1 megavolt¹) that requires specific electrical insulation.
A set of dedicated buildings nearby will host the multistage conversion process of the electrical current coming from the 400 kV switchyard—first from AC to DC, then to AC again in order ensure stability, and finally to DC again.
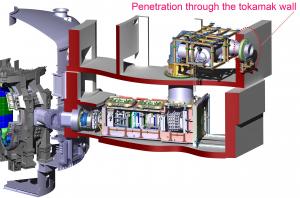
The size of the neutral beam injectors is apparent in this drawing, which shows them in relation to the vacuum vessel (at left). The transmission lines, which must travel through the wall of the Tokamak Building, are correspondingly massive.
The transmission lines will range from 80 to 150 metres in length, depending on the location of the circular openings. Once they pass through the concrete wall of the Tokamak Building, they will take a 90-degree turn to plunge down to the injectors (see drawing).
The ITER neutral beam injection system will be able to deliver approximately one-third of the total heating power needed to bring the plasma to fusion temperature.
¹One megavolt is more than twice the capacity of high-voltage overhead power lines.