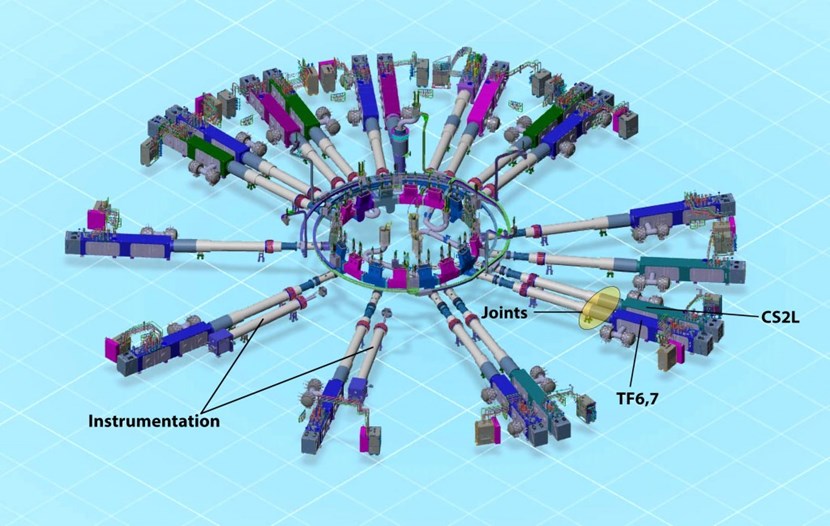
Of 21 feeders installed in galleries at the B2 level of the Tokamak Building, two accommodate high and low-voltage instrumentation cables and hardware. Ten other feeders are located five floors overhead, at the L3 level.
Over the ensuing years the main elements that constitute a feeder were progressively installed in the galleries of the Tokamak Building. At the B2 level, 16 coil terminal boxes the size and weight of a city bus, and 18 cryostat feedthroughs that pass through the bioshield and cryostat to be connected to the coils are now fully installed and welded. At the L3 level, 6 coil terminal boxes and 8 cryostat feedthrough have been lifted and placed in long-term temporary positions, pending the insertion of the cryostat's upper cylinder.
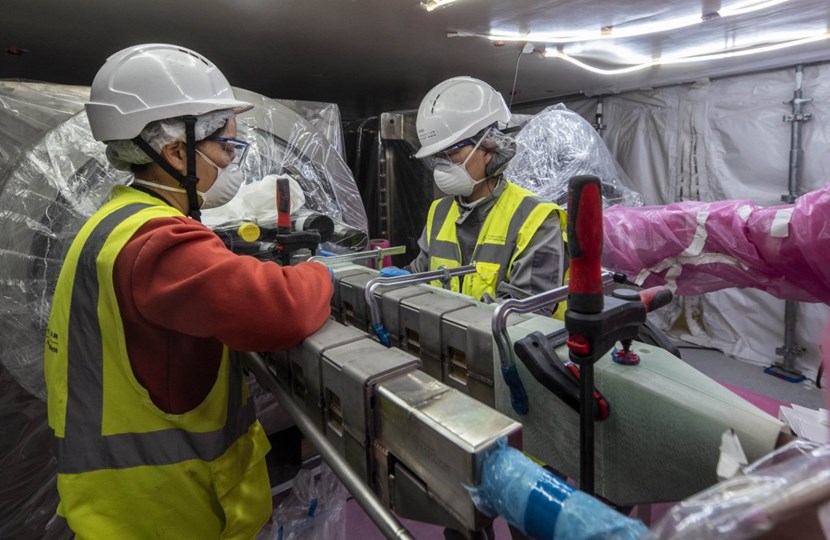

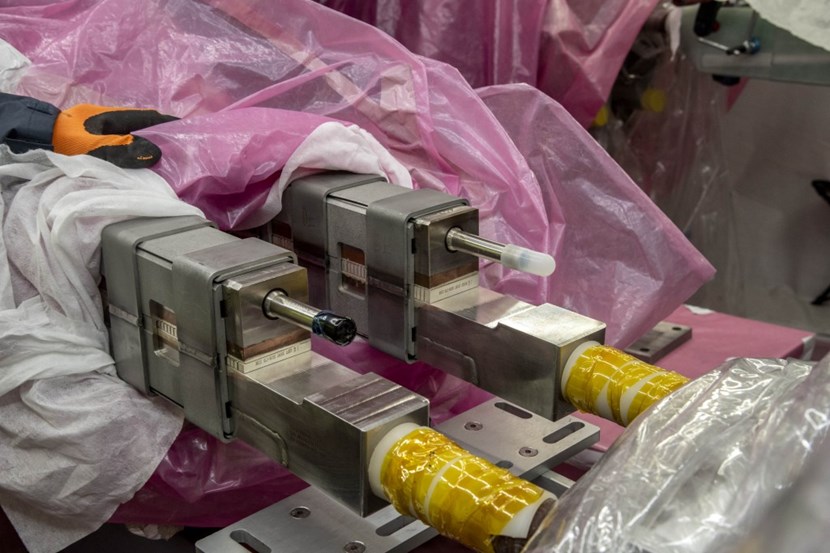
At the second basement level (B2) of the Tokamak Complex, highly skilled workers from the CNPE consortium are finalizing the joints on the feeder connected to the lowest central solenoid module (CS2L).
One of the most delicate operations in the installation process is the creation of the 








